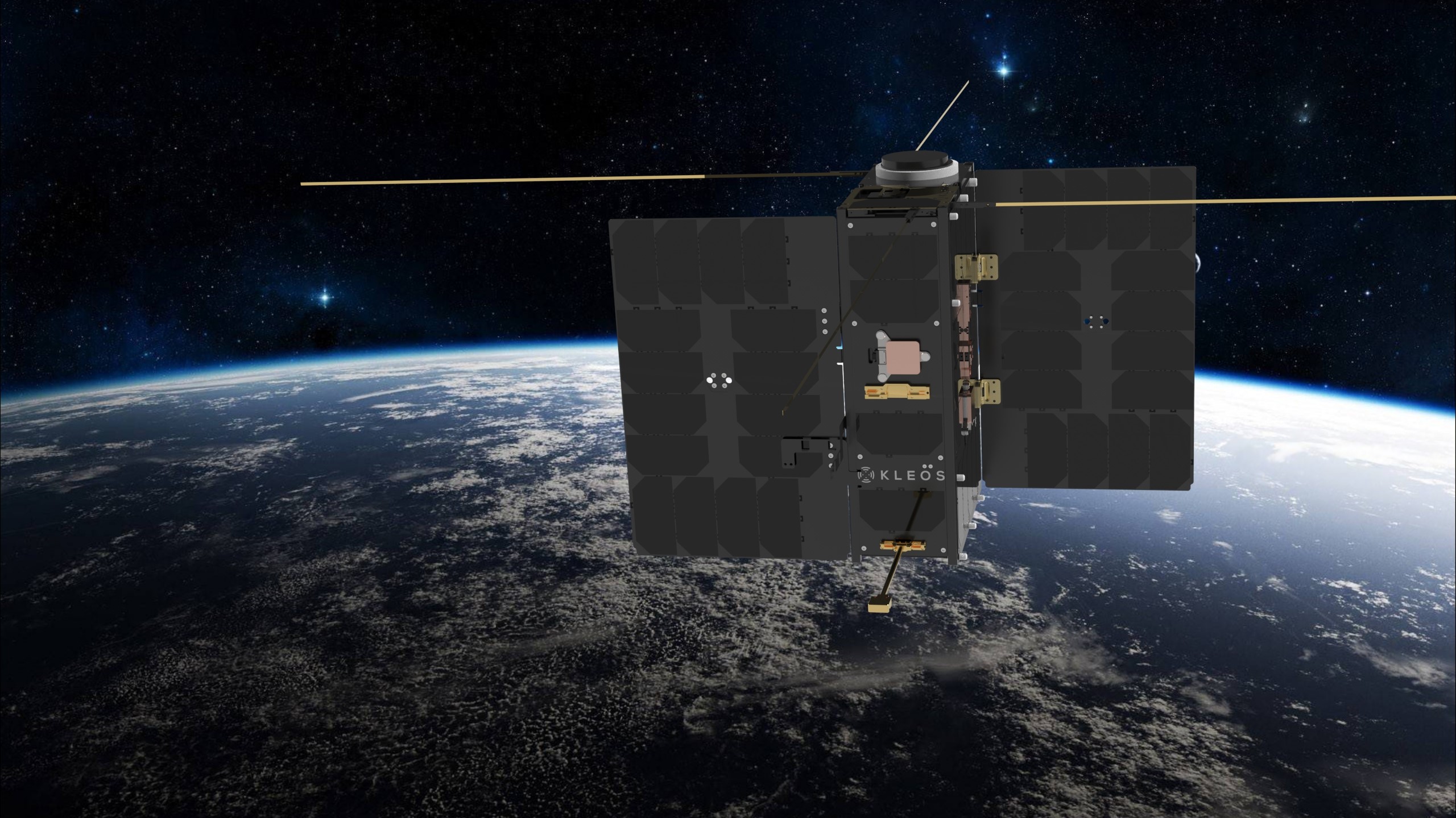
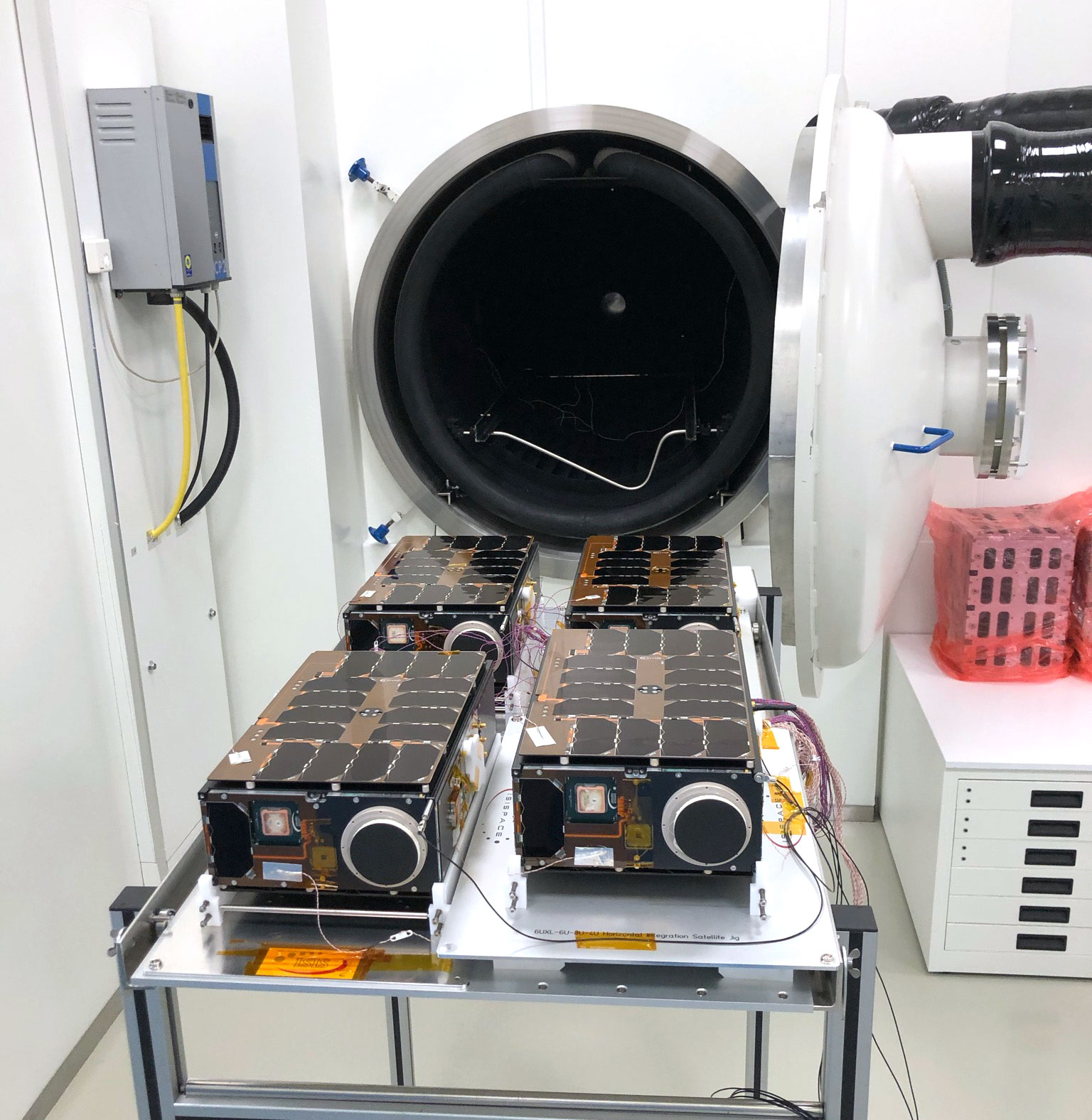
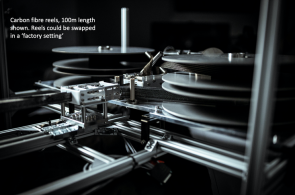
One of the secrets to Kleos’ technological agility and lower costs when compared to traditional collect capabilities comes down to its use of nanosatellites—satellites with a mass under 10 kilograms.
That’s because these smaller satellites are cheaper to produce, faster to build, and quicker to launch. The rapid development cycle allows Kleos to put the most up-to-date technology onboard with each new satellite build. Nanosatellites are also well-suited for constellations, which allow Kleos to cost-effectively cover more area with more frequent revisit.
A little satellite History
Large, complex satellites—those above 4,200 kilograms—have dominated the commercial space market since 1960. They are highly capable and usually have long service lives, but they are expensive to build, with large payloads and long production timelines. Though technological advances have improved the efficiency of large satellites, the space market required an alternative. Enter nanosatellites.
The trend of small satellites has emerged as a key advancement in space technology, according to the latest Joint Operating Environment report (JOE 2035).
“These advances will likely lead to improved reliability, with networks of small satellites and stratospheric swarms performing the tasks previously reserved exclusively for large satellites.”
A clear choice
The use of nanosatellites is in Kleos’ DNA. The company was founded on a recognition that the economic requirements of space-based systems have fundamentally changed in the last ten years, opening up an entirely new set of opportunities for remote sensing with short development times and lower costs than previously possible.
By choosing a more responsive technology, Kleos can evolve to meet the changing requirements of the space market. For example, they can offer a flexible approach to future launch plans, with the opportunity for customers to request the collection of specific RF bands, coverage areas, and other collection parameters. For new collection missions, Kleos can move from concept development and requirements to full deployment and data, in as little as nine months, which is significantly faster than traditional satellite systems.
The use of nano-satellites allows flexibility to develop and integrate new technology quickly to enhance Situational Awareness, establish land and sea border control, support regulatory framework monitoring, aid search and rescue, establish conditions for better resource management, fisheries monitoring, monitoring of illegal trafficking, smuggling & illegal transhipments, and support embargo and sanctions enforcement among other use cases.
IN addition, nano-satellites allow Kleos to:
- Be more flexible in terms of its services and roadmap
- Have a more agile, responsive approach to market demand
- Plan and deploy mission specific clusters quickly
- Bring new collection capabilities to space within a year
Rapidly deployed nano satellite technology ensures data offerings that can meet customer and market demand. Kleos’ roadmap includes deployment of additional clusters in short timeframes to support of a wide number of intelligence, defence, security, and commercial missions. The company plans to operate at least 20 clusters.